Why Does Delhi Keep Shaking? Tectonic Stress Triggers 4.4 Magnitude Earthquake in Jhajjar
Delhi-NCR experienced yet another seismic jolt on Thursday morning as a magnitude 4.4 earthquake struck Jhajjar, Haryana, at 9:04 AM, causing strong tremors across Noida, Gurugram, Ghaziabad, Faridabad, and even reaching Meerut and Shamli in western Uttar Pradesh.
Why?
This recurring seismic activity is no coincidence — Delhi sits at the edge of a geological collision zone where the Indian tectonic plate pushes against the Eurasian plate, building up stress that releases as earthquakes.
Report:
According to the National Center for Seismology (NCS), the earthquake originated at a depth of 10 km, located at 28.59°N, 77.16°E, about 9 km east of New Delhi. Though classified as moderate, the quake was widely felt and shook buildings, prompting many to rush outdoors. Residents reported shaking ceiling fans, swaying lights, and vibrating computer screens — with many calling it the longest quake they've felt in years.
Expert’s opinion:
Experts say Delhi’s frequent tremors are linked to its position in Seismic Zone IV, a high-risk classification due to the presence of active fault lines like the Delhi-Haridwar Ridge, Sohna Fault, and Delhi-Moradabad Fault.
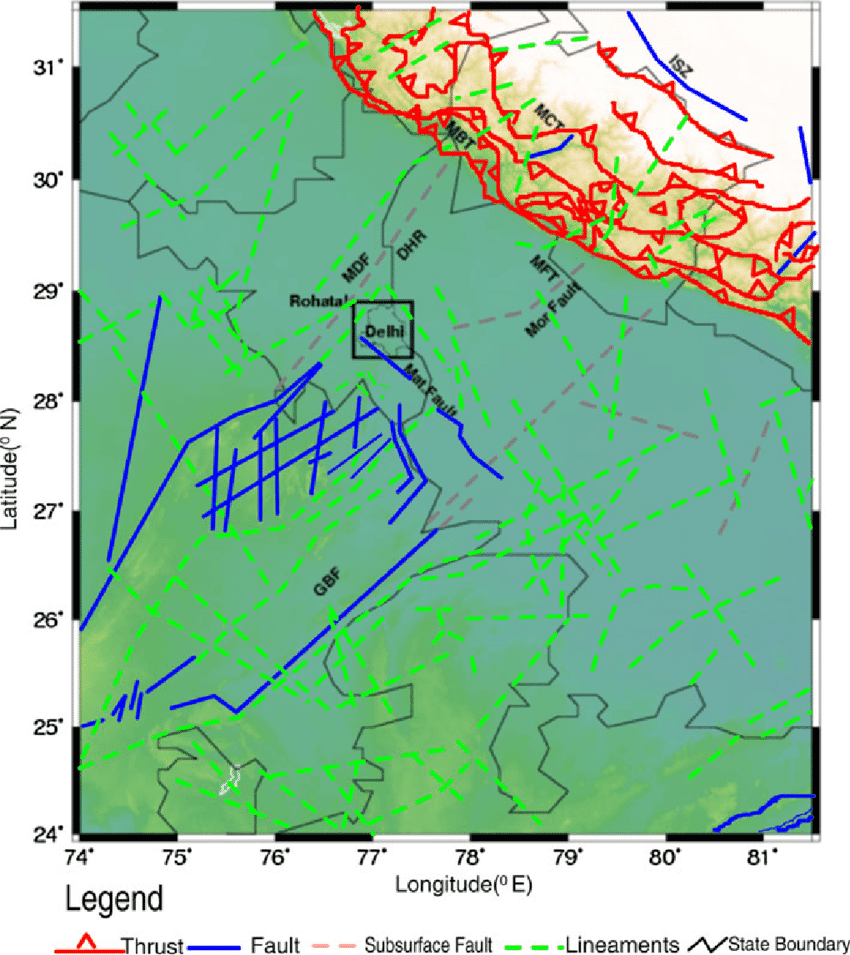
This map illustrates the major tectonic features around Delhi-NCR, including the Delhi–Haridwar Ridge, Sohna Fault, and Moradabad Fault. These geological structures define the region's seismic vulnerability and help explain the recurring tremors.
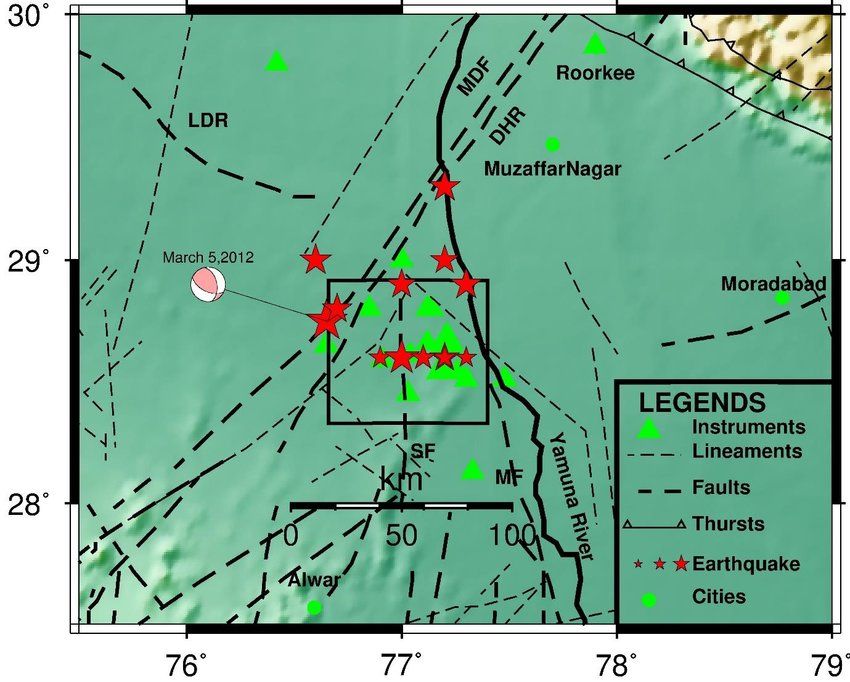
A seismotectonic map showing active fault lines and historical earthquake epicenters in Delhi-NCR. The cluster of past quakes along the Sohna and Delhi-Moradabad faults highlights their ongoing seismic activity.
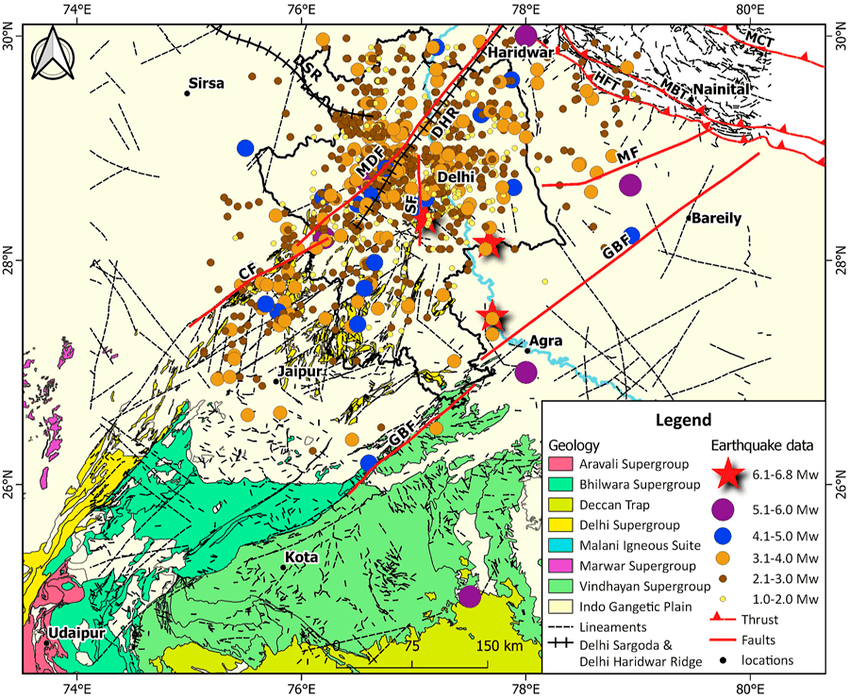
This diagram shows the subsurface crustal structure beneath Delhi, revealing buried faults like the Delhi-Haridwar Ridge and the dynamic interaction of tectonic blocks. These hidden fractures store stress that can trigger earthquakes.
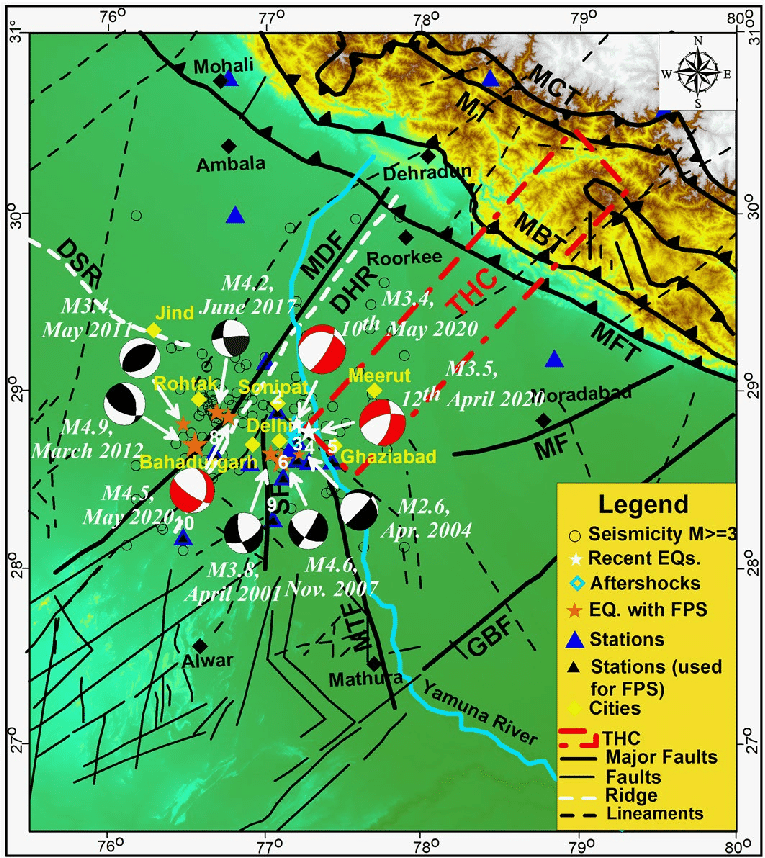
A high-resolution satellite-based map identifying active faults and lineaments in NCR. Features like the Sohna Fault are marked as seismically significant, with surface traces aligned with regional tremor patterns.
All images are sourced from ResearchGate and scientific journals for educational use.
These underground fractures are under constant pressure from tectonic forces. Over time, stress builds until it’s suddenly released — causing the ground to shake, sometimes without warning.
The National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) issued an advisory shortly after the tremor, urging people to evacuate calmly using stairs and avoid panic.
No damage or injuries have been reported so far. However, seismologists and urban planners stress the urgent need for earthquake preparedness, building code compliance, and public awareness, especially in densely populated, high-risk areas like Delhi-NCR.













